Resources included in these libraries were submitted by ITEST projects or STELAR and are relevant to the work of the NSF ITEST Program. PDFs and/or URLs to the original resource are included in the resource description whenever possible. In some cases, full text publications are located behind publishers’ paywalls and a fee or membership to the third party site may be required for access. Permission for use must be requested through the publisher or author listed in each entry.
Thinking and Drinking Critically: A Unit on New York City’s Water Quality
Publication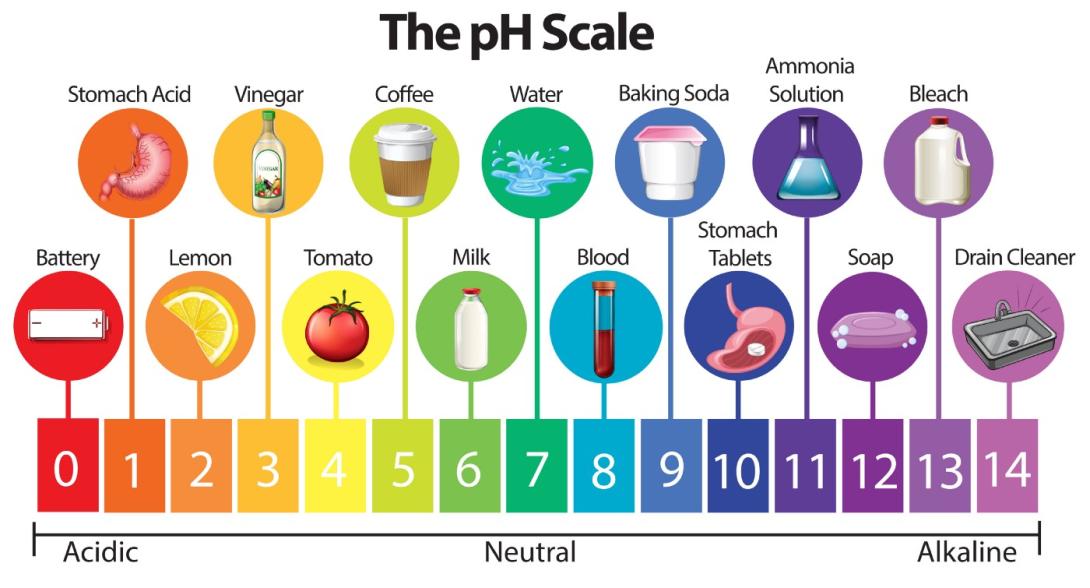
The Flint, Michigan water crisis drew national attention to the effects of unsafe drinking water and issues of equity and social justice. It also opened up opportunities for engaging in socio-scientific issues in the science classroom (Ewing and Sadler 2020). Students consume hundreds of gallons of water daily, but do they know where their drinking water comes from and if it’s always safe to drink? A three-dimensional unit designed for upper elementary students (in this case, fourth graders) helps students answer these questions. Students follow the incredible journey of New York City’s water
Developing and Popularizing STEM Online Tools: The Case of 'Listening to Waves' Tools for the Science of Music
PublicationMusic is a source of joy and identity formation in all cultures and socio-economic strata, and its connections with science, technology, engineering, and math are numerous. One important connection is with the physics of waves. Listening to Waves (LTW) is a program designed to increase adolescents’ interest in STEM through the science of sound and music. Based on LTW’s early experience performing STEM outreach activities in schools, LTW recognized the need to create easily accessible tools for visualizing and manipulating sound. In particular, LTW has been developing browser-based
Making Mathematics Relevant: an Examination of Student Interest in Mathematics, Interest in STEM Careers, and Perceived Relevance
PublicationCommunity college students face difculties in mathematics courses and may not understand the relevance of the topics they are learning to their intended career. When such connections are not made, mathematics courses can become barriers to pursuit of careers in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM). In the present study, we assessed student interest in mathematics and various STEM career areas and students’ knowledge of ways mathematics was involved in STEM careers in order to better understand how these variables are related. We discovered that interest in mathematics
Making Mathematics Relevant: an Examination of Student Interest in Mathematics, Interest in STEM Careers, and Perceived Relevance
PublicationCommunity college students face difculties in mathematics courses and may not understand the relevance of the topics they are learning to their intended career. When such connections are not made, mathematics courses can become barriers to pursuit of careers in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM). In the present study, we assessed student interest in mathematics and various STEM career areas and students’ knowledge of ways mathematics was involved in STEM careers in order to better understand how these variables are related. We discovered that interest in mathematics
Simulation Technology and Student Engagement
PublicationAn authentic learning environment with the integration of technology can effectively engage students and improve their academic performance. Technology can support learning situations that relate to real life, and provide opportunities for inquiry and collaboration, fostering engagement. This paper will provide details of an authentic learning environment that utilizes flight simulation software to engage middle school students in the learning of several math and science concepts. Active learning lessons were developed using missions flown on the flight simulator. The pedagogical approach was
Engagement in Practice: STEM Engagement through Mentoring
PublicationThe declining levels of U.S. student achievement in mathematics and science were brought into focus by the President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology, which stated that the U.S., especially at the elementary and secondary levels, is struggling to remain competitive with other nations in STEM education (PCAST, 2010). Furthermore, according to a report issued by the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NCES, 2015), less than 30 percent of students enrolled in the U.S. are proficient in the areas of science or mathematics. The landscape becomes more troubling when one
Spreading GIS-Infused Instruction: A Cross-Case Comparison of Two Instructional Approaches
PublicationThis work is part of an ongoing partnership that seeks to create a sustainable infrastructure to support GIS-infused instruction in a large urban school district. In this paper, we report an illustrative cross-case comparison of two teachers’ approaches to infusing GIS in their courses. The goal of this analysis is to examine how GIS-infused instruction is adapted in different contexts and to consider the affordances of divergent approaches. Findings illustrate the relationships among organizational context, individual and collective context, particularly teacher identity, and instructional
Correlation of STEM Interest and Career Intent in High-School Students
PublicationUnderstanding high school students’ perceptions and dispositions toward STEM, and the role science and math self-efficacy play in establishing STEM career aspirations is imperative to preparing the STEM workforce of the future. Project STEMulate is an industry-aligned technology-rich Problem-Based Learning (PBL) model. The goal of this NSF ITEST grant-funded study (2018-2020) was to improve students’ attitudes towards STEM. Project STEMulate focuses on Upward Bound students in Hawai'i and was implemented at three sites: University of Hawaiˋi (UH) Maui College, UH Hilo, and Windward Community
Mapping Students’ Engineering Processes with Design Zones
Publication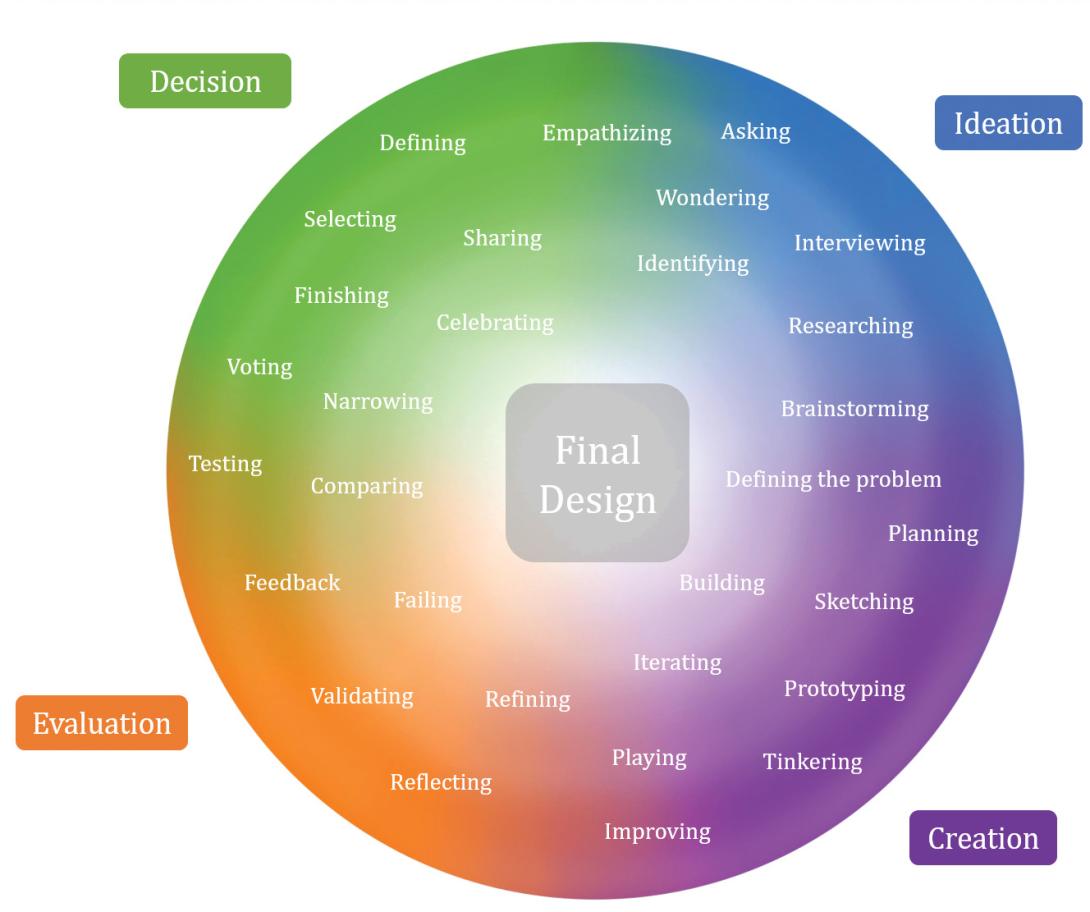
The engineering design process (EDP) can be a wonderful tool to nurture creative problem-solving abilities, prepare students to tackle problems with intentional planning, and encourage learning from failures. Many lesson plans and instructional strategies are guided by the EDP (Hill Cunningham, Mott, and Hunt 2018). Visual representations of the EDP often show a set of actions arranged in a cycle. For example, many of you are probably familiar with the Engineering is Elementary graphical aid that shows five labeled steps, “Ask, imagine, plan, create, improve” (Museum of Science, Boston 2020)
Impacting Teacher and Counselor Practices as They Support Traditionally Underrepresented Students to Pursue STEM Majors and Careers
PublicationThis Innovative Practice Work in Progress paper presents Catalyzing Inclusive STEM Experiences All Year Round (CISTEME365), a multi-year project funded by the National Science Foundation. We designed a networked community of middle/high school teachers, counselors, and administrators focused on improved understanding and promoting practices that increase students' motivations and capacities to pursue science, engineering, technology, and mathematics (STEM) careers. We also collaborated with them to implement out-of-school-time STEM clubs that provide engineering design, project-based, and